Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Psoriasis Treatment: Exploring Effective Therapies, Innovative Approaches, and Self-Care Strategies for Healthier Skin
psoriasis treatment
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by red, inflamed patches covered with silvery scales, psoriasis can cause significant discomfort and affect a person’s quality of life. Fortunately, various treatments can help manage the symptoms and improve skin health. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different treatment options for psoriasis, including topical psoriasis treatment, systemic medications, phototherapy, and innovative approaches. Additionally, we will discuss self-care strategies to support overall well-being and skin health.
Understanding Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, causing rapid skin cell turnover. This results in the formation of thick, scaly patches known as plaques. Psoriasis can affect any part of the body but is commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. The severity of psoriasis can vary from mild to severe, and it can sometimes lead to complications such as psoriatic arthritis.
Types of Psoriasis
There are several types of psoriasis, each with distinct characteristics:
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most common type, characterized by raised, red patches covered with a silvery-white buildup of dead skin cells.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Appears as small, dot-like lesions, often triggered by bacterial infections like strep throat.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Occurs in skin folds such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts, causing smooth, red lesions.
- Pustular Psoriasis: Characterized by white pustules surrounded by red skin, it can be localized or widespread.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A severe form causing widespread redness and shedding of the skin, often requiring immediate medical attention.
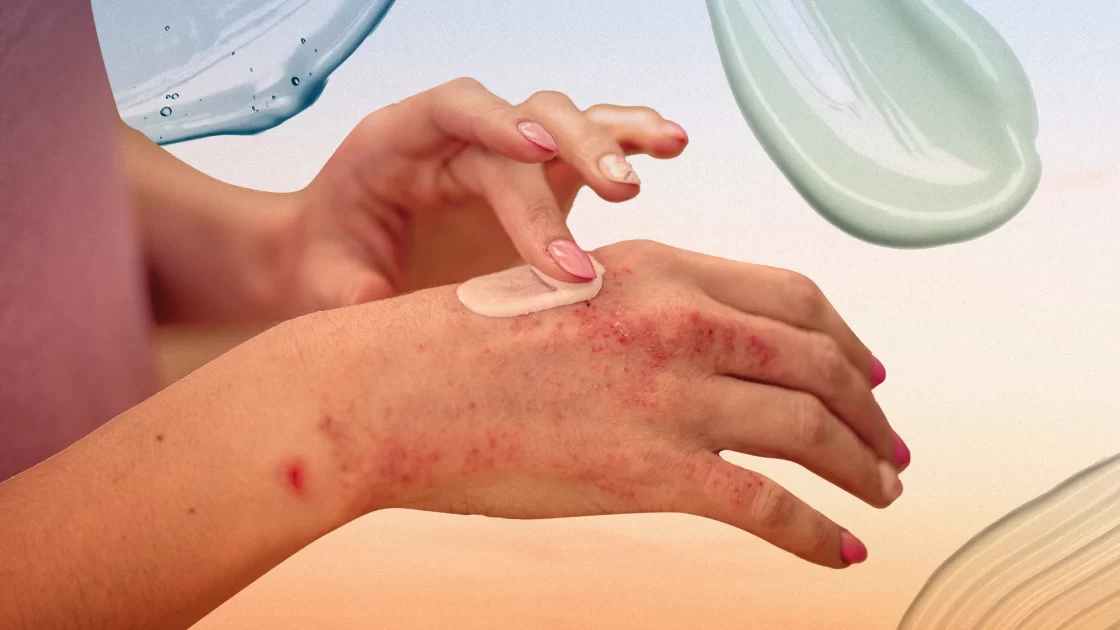
Topical Treatments for Psoriasis
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense in managing mild to moderate psoriasis. These treatments are applied directly to the affected skin areas and can help reduce inflammation, slow down skin cell production, and alleviate itching.
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory medications come in various strengths and are available as creams, ointments, lotions, and foams. They help reduce inflammation and relieve itching.
- Vitamin D Analogues: Synthetic forms of vitamin D, such as calcipotriene and calcitriol, can slow skin cell growth and reduce scaling.
- Retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, topical retinoids like tazarotene can help normalize skin cell production and reduce inflammation.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are used off-label for psoriasis and are particularly effective in sensitive areas like the face and groin.
- Coal Tar: An older treatment, coal tar can help reduce scaling, itching, and inflammation. It is available in various formulations, including shampoos for scalp psoriasis.
- Salicylic Acid: This peeling agent helps remove scales and can be used in combination with other topical treatments to enhance their effectiveness.
Systemic Medications
For moderate to severe psoriasis, systemic medications may be necessary. These medications work throughout the body and are usually prescribed when topical treatments are not effective or when psoriasis affects large areas of the skin.
- Methotrexate: An oral medication that suppresses the immune system, reducing skin cell production and inflammation. It can have significant side effects, so regular monitoring is required.
- Cyclosporine: Another immunosuppressant, cyclosporine is effective in controlling severe psoriasis but is generally used for short-term treatment due to potential kidney damage and high blood pressure.
- Acitretin: An oral retinoid, acitretin is used for severe psoriasis and helps normalize skin cell growth. It can cause birth defects, so it is not recommended for women of childbearing age unless effective contraception is used.
- Biologics: These are newer, targeted treatments made from living organisms. They work by blocking specific parts of the immune system. Common biologics for psoriasis include adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, and ustekinumab.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy, or light therapy, involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision. It is an effective treatment for moderate to severe psoriasis.
- UVB Phototherapy: Involves exposing the skin to UVB light, either through a lightbox or targeted laser. It helps slow down skin cell growth and reduce inflammation.
- PUVA Therapy: Combines UVA light with a photosensitizing medication called psoralen. PUVA is effective for severe cases of psoriasis but can increase the risk of skin cancer with long-term use.
- Excimer Laser: A form of targeted phototherapy, the excimer laser delivers concentrated UVB light to specific areas of the skin, minimizing exposure to healthy skin.
Innovative Approaches to Psoriasis Treatment
Advances in medical research have led to the development of innovative treatments for psoriasis. These approaches offer new hope for those who have not responded well to traditional therapies.
- Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitors: These oral medications, such as tofacitinib, block specific pathways involved in the inflammatory process, offering a new option for treating moderate to severe psoriasis.
- Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) Inhibitors: Apremilast is an oral medication that reduces inflammation by inhibiting the PDE4 enzyme. It is effective for both psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
- Microbiome-Based Treatments: Research into the skin microbiome has led to the exploration of probiotics and prebiotics as potential treatments for psoriasis. These therapies aim to restore the balance of beneficial bacteria on the skin and reduce inflammation.
- Gene Therapy: While still in the experimental stages, gene therapy holds promise for treating psoriasis by targeting specific genes involved in the disease process.
Self-Care Strategies for Managing Psoriasis
In addition to medical treatments, self-care plays a crucial role in managing psoriasis and improving overall well-being. Here are some self-care strategies to consider:
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the skin moisturized helps reduce dryness, scaling, and itching. Use thick, fragrance-free moisturizers and apply them immediately after bathing.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid triggers that can worsen psoriasis, such as stress, smoking, alcohol, and certain medications. Keeping a journal can help track triggers and flare-ups.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can support overall health and reduce inflammation.
- Practice Stress Management: Stress can trigger or worsen psoriasis flare-ups. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or hobbies that bring joy.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps keep the skin hydrated and may improve the overall condition of the skin.
- Protect Your Skin: Avoid harsh soaps and hot water, as they can irritate the skin. Use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and take lukewarm baths instead of hot showers.
- Get Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help reduce stress, improve mood, and support a healthy immune system. Choose low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Join a Support Group: Connecting with others who have psoriasis can provide emotional support, share coping strategies, and offer a sense of community.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a complex and chronic condition that requires a multifaceted approach to treatment and management. While there is currently no cure for psoriasis, various treatments and self-care strategies can help control symptoms and improve quality of life. By working with a healthcare provider and exploring the options available, individuals with psoriasis can find an effective treatment plan tailored to their needs.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide valuable information on the different treatment options for psoriasis, from topical treatments and systemic medications to innovative therapies and self-care strategies. By understanding the available treatments and taking proactive steps to manage the condition, individuals with psoriasis can achieve healthier skin and a better quality of life.